Schalal
Towards Open Vocabulary Learning: A Survey
传统计算机视觉算法依赖于封闭数据集–>目标检测、分割和追踪只能在数据集对应的有限的类别集合上进行,而现实世界的目标类别远超过这些有限的类别 –> 视觉语言模型的发展促进开放式词汇方法的发展。
1 Introduction
- 传统CV方法
- 零样本学习(Zero-shot Learning, ZSL):通常使用词嵌入,训练解码器通过已知类别判别未知类别(词嵌入方法 based on their pre-defined word embeddings,无法利用视觉信息和关系信息)
- Open vocabulary learning与ZSL的区别在于其可以利用visual-related language vocabulary data(如图片标题)作为辅助监督项:文本数据更易label(与图片mask相比),更extendable和general
- VLM(Visual Language Model):将图片特征和文本特征对齐到同一空间,开放词汇学习通常会用到VLM学习到的alignment
-
本文的内容:少样本学习、多模态学习、视觉语言预训练 目标检测、分割、视频理解、三维场景理解 与ZSL、开放集识别(open-set recognition,OSR)、分布外检测(out of distribution detection,OOD)
2 Background
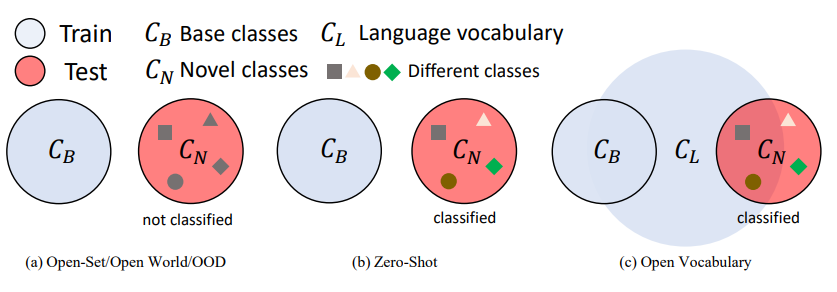
(novel classes就是OOD examples)
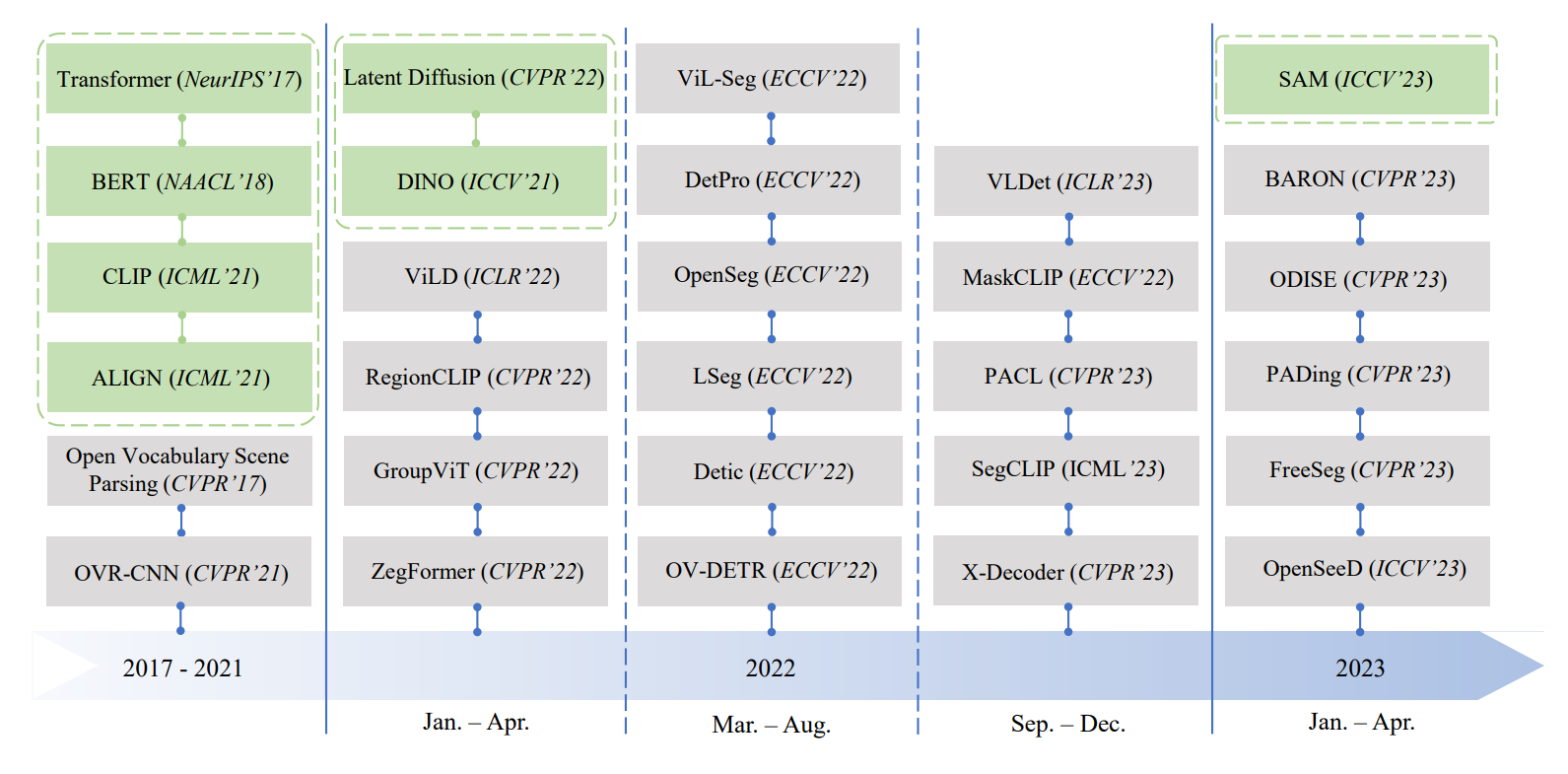
(绿色的是基础技术)
Methods
preliminary
- pixel-based:语义分割、实例分割
- query-based:vision transformer
VLM
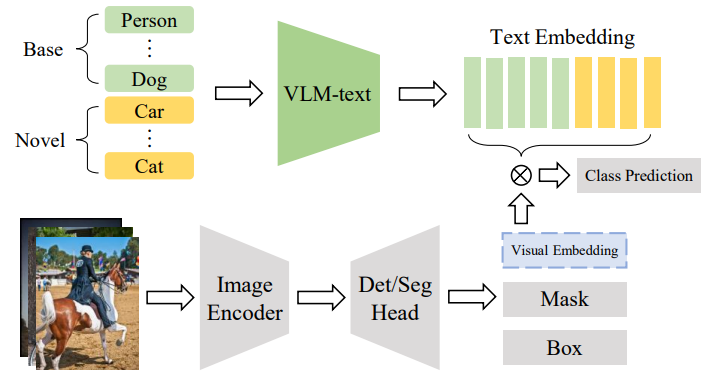
- large scale visual langauge pre-training: 2-stream network
- turning close-set detector and segmenter into open vocabulary settings.
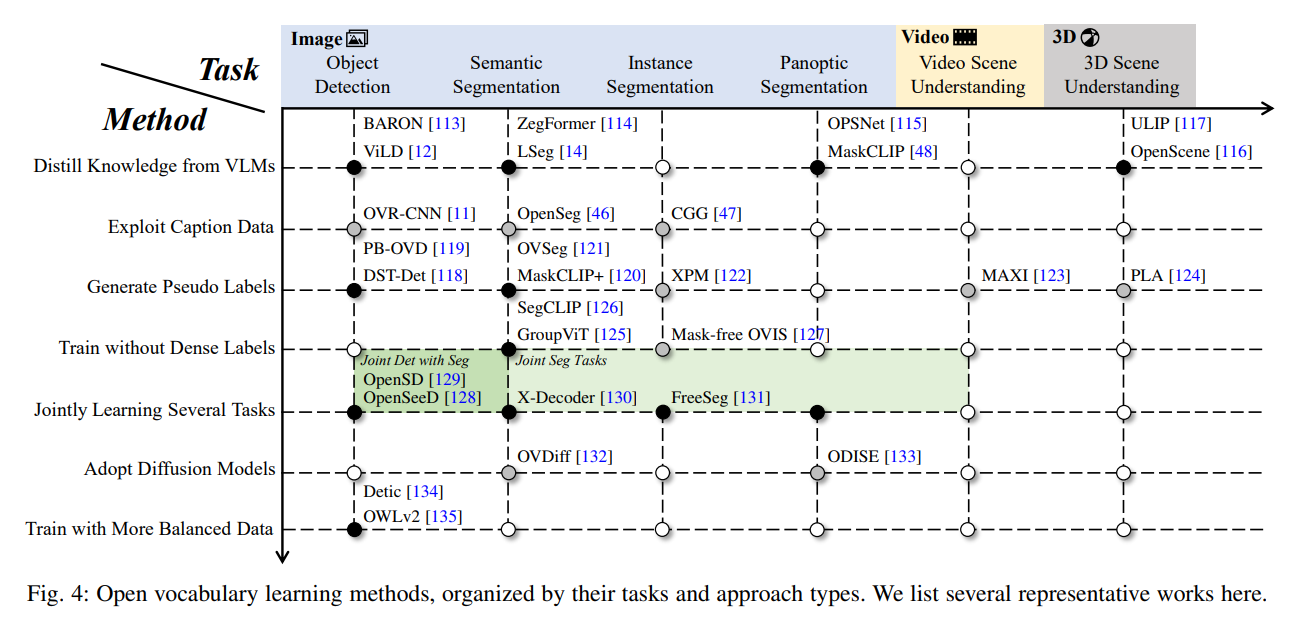
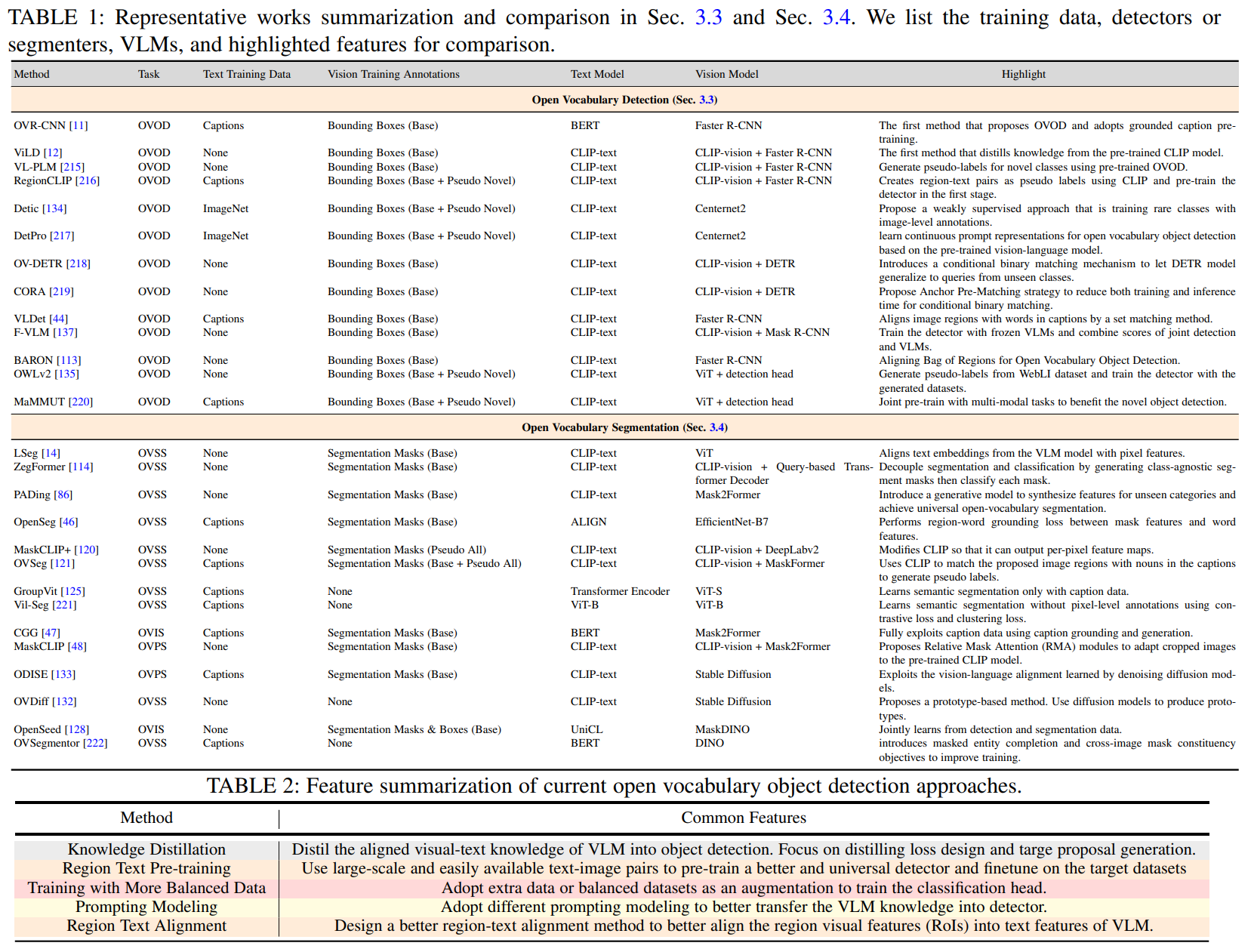
open vocabulary object detection
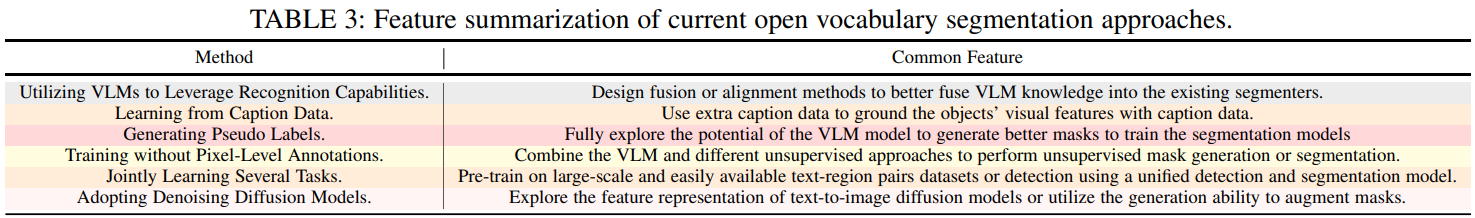
open vocabulary segmentation
open vocabulary video understanding
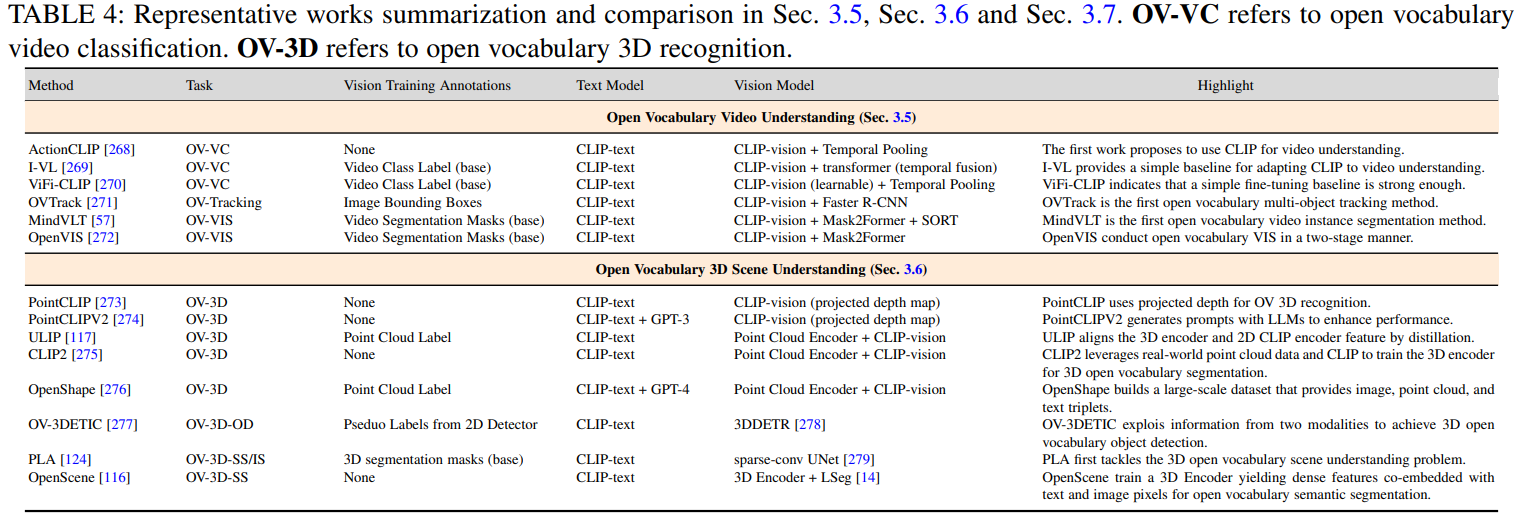
open vocabulary 3d understanding
- 3D recognition: 点云分类和分割:先投影到二维,然后再进行图片的类似操作;改进:改进投影方式,缝合额外的解码器,组合多模态数据(点云+图像+文本)
- 3D object detection
- 3D scene understanding
closely related tasks
- Class Agnostic Detection and Segmentation: 不明确划分类别(所谓class agnostic),只输出score,可能提升泛化能力
- Open World Object Detection: 标注novel category为unknown
- Open-Set Panoptic Segmentation: 全景分割,标注novel category
Chanllenges and Outlook
- 挑战:base classes过拟合;训练成本过高;跨数据集评估存在性能差异;已有类别存在概念上的重叠
- 展望:探索时序信息;直接的3D open vocabulary 场景理解;制备基础模型 for 自定义任务的特定调整(in-context model,连接VLM和LLM);与增量学习的组合;与大语言模型的组合